Casemates
Vereinfachung und Verbesserung des Zugriffs auf den SPARQL-Endpoint «Casemates», um die Daten des Bundesrechts beziehen zu können
Mit diesem Projekt soll der Zugang zu den Daten des Bundesrechts für Firmen und Interessierte über die Abfragesprache SPARQL vereinfacht und das Verständnis sowie die Möglichkeiten zum Zugriff auf Casemates und die Daten des Bundesrechts verbessert werden. Verschiedene Firmen arbeiten bereits mit dem SPARQL-Endpoint des Bundesrechts und beziehen von dort Daten, um diese in eigene Anwendungen zu übernehmen. Die Möglichkeiten, die der Endpoint bietet, werden derzeit jedoch noch nicht in dem Masse genutzt, wie dies möglich wäre. Das Potential ist entsprechend gross.
Wir haben mit SPARnatural https://github.com/sparna-git/Sparnatural/ einen Query Builder erarbeitet, der zur Zeit mit Luxemburgischen Daten funktionert (Fedlex basiert auf der Luxemburger Anwendung): https://ribeaud.github.io/Sparnatural/demos/sparnatural-demo-legilux/index.html
Wir deckten Teile der "Geheimwissenschaften" des SPARQLn auf: Die semantische Strukturen der Daten können statisch, wie auch dynamisch abstrahiert werden.
Ein schöner Querybuilder ist z.B.: https://query.wikidata.org/ Leider sind der Querybuilder und der Queryservice zu sehr mit der Wikiwelt verbunden.
Ausblick: Die Bundeskanzlei ergänzt nun ihre Datenstruktur am Casemates-SPARQL-Endpoint soweit auf, dass Querybuilder damit umgehen können. Auch werden die Daten ab Sommer im XML AKN Format https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Akoma_Ntoso zur Verfügung gestellt (gilt für Publikationen ab Sommer 2022).
Bei SPARQL handelt es sich um eine graphenbasierte Abfragesprache. Das Akronym SPARQL steht dabei für "SPARQL Protocol And RDF Query Language".
SPARQL wird im Rechtsumfeld mehr und mehr genutzt und kommt zum Beispiel auch bei dem Linked Data Service (https://lindas.admin.ch/) des Bundesarchivs zum Einsatz. Auch Geodaten von swisstopo werden per SPARQL angeboten.
SPARQL wird jedoch noch nicht in gleichem Masse wie andere Abfragesprachen gelehrt. Das Erstellen von SPARQL-Abfragen und damit der Zugriff auf Daten fällt daher häufig vergleichsweise schwer. Viele SPARQL/Semantic Web Lernresourcen sind auf https://www.poolparty.biz/resource-library einsichtbar.
Sparnatural - A natural way of building SPARQL queries
Sparnatural is a visual SPARQL query builder written in javascript.
It supports the creation of basic graph patterns with the selection of values with autocomplete search or dropdown lists. It can be configured through a JSON-LD or OWL configuration file (that can be edited in Protégé) that defines the classes and properties to be presented in the component.
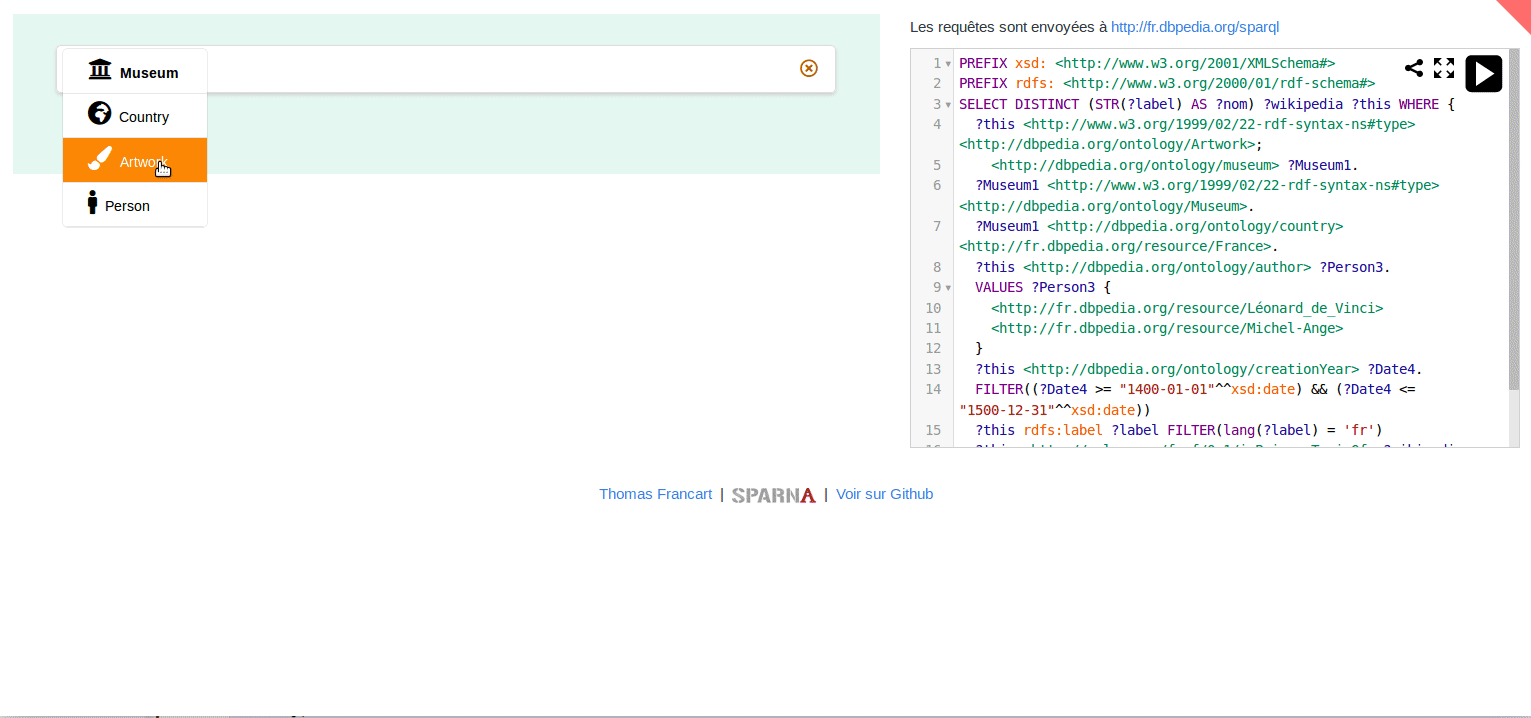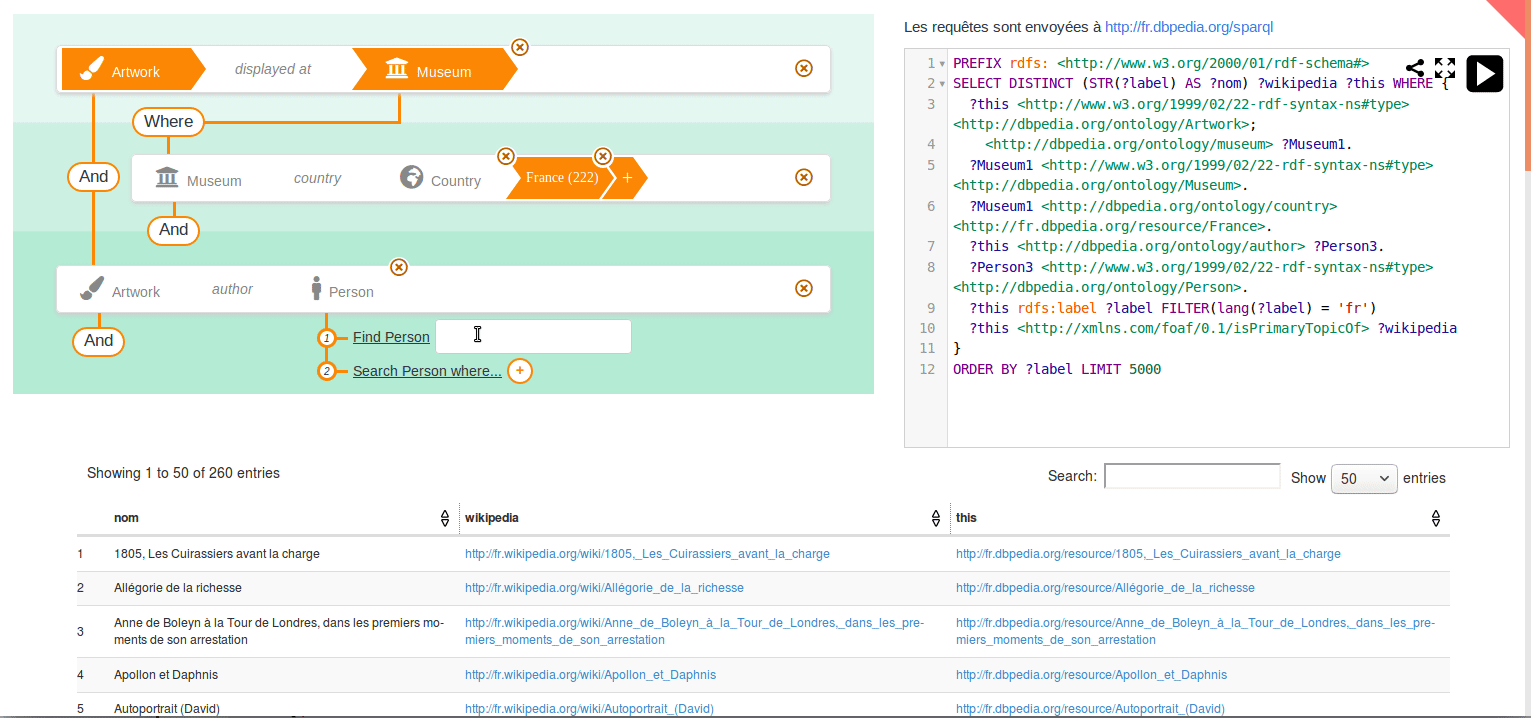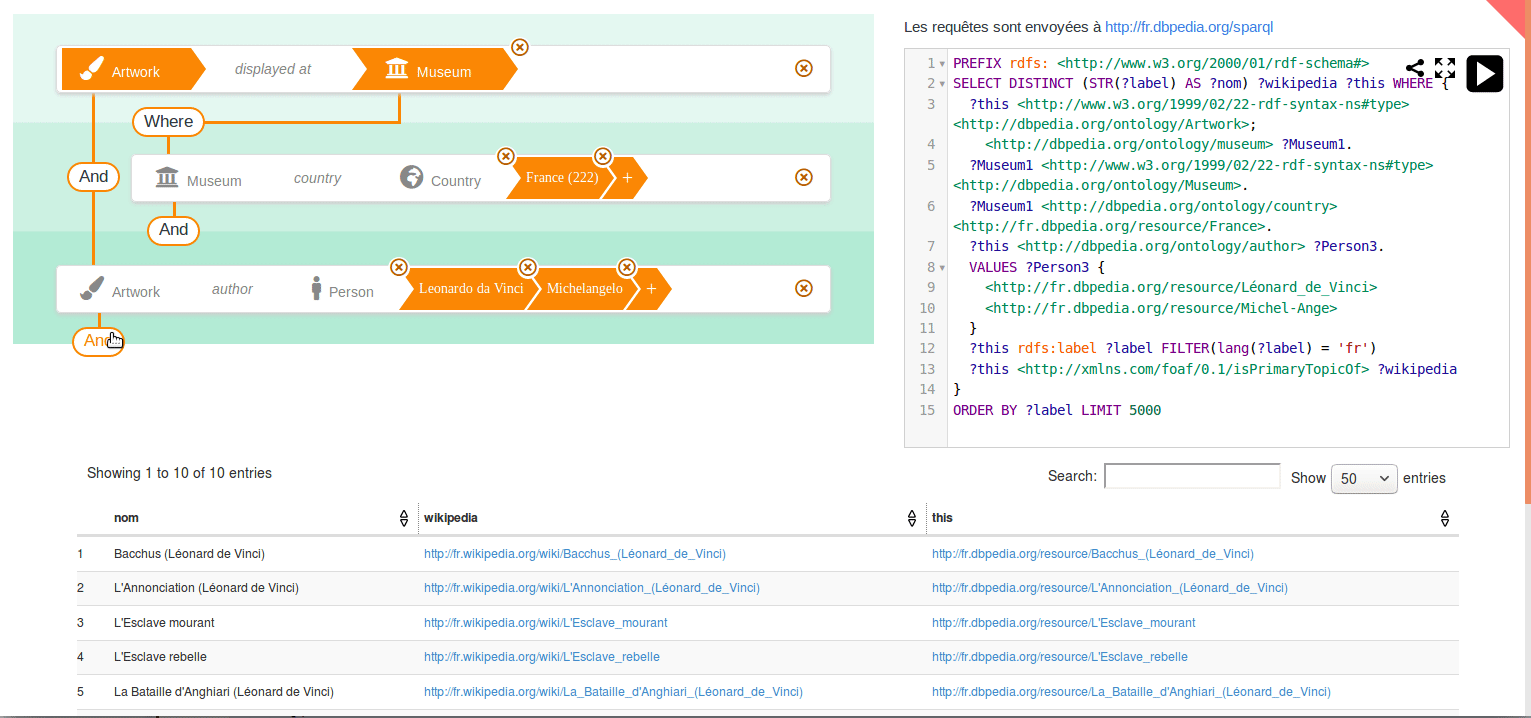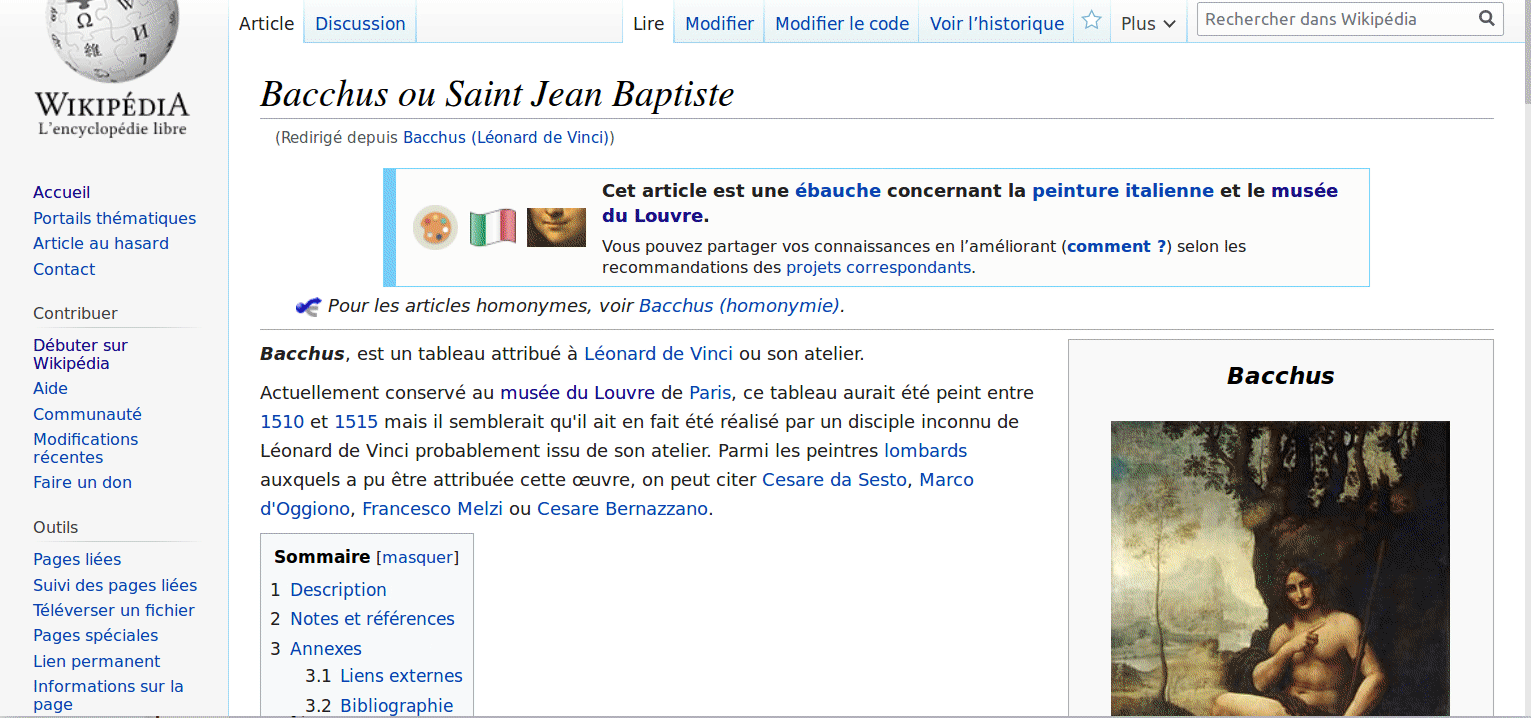
You can play with online demos at http://sparnatural.eu#demos.
Getting Started
To get started :
- Read the following documentation;
- Read the Wiki
- Look at how things work in file
sparnatural-demo-dbpedia/index.html; - In particular look at how the specifications are written by looking at the source of
sparnatural-demo-dbpedia/index.html - Adapt
sparnatural-demo-dbpedia/index.htmlby changing the configuration and adapting the SPARQL endpoint URL;
To get started with docker :
- Clone the git repository
- Run
docker-compose build - Run
docker-compose up - Open your browser: http://127.0.0.1:8080
Features
Query Structure
Basic query pattern
Select the type of entity to search...
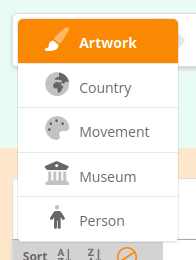
... then select the type of the related entity.
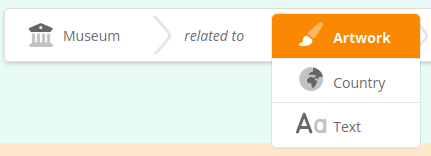
In this case there is only one possible type of relation that can connect the 2 entities, so it gets selected automatically. Then select a value for the related entity, in this case in a dropdown list :
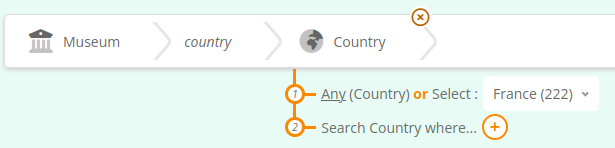
Congratulations, your first SPARQL query criteria is complete !

Now you can fetch the generated SPARQL query :

"WHERE"
This enables to navigate the graph :
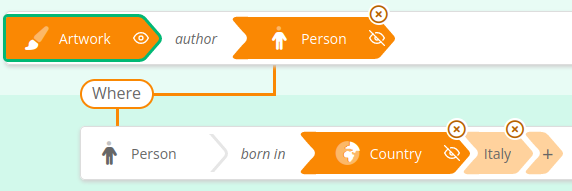
"AND"
Combine criterias :
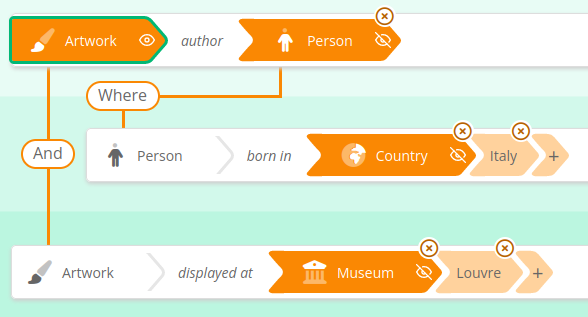
"OR"
Select multiple values for a criteria :
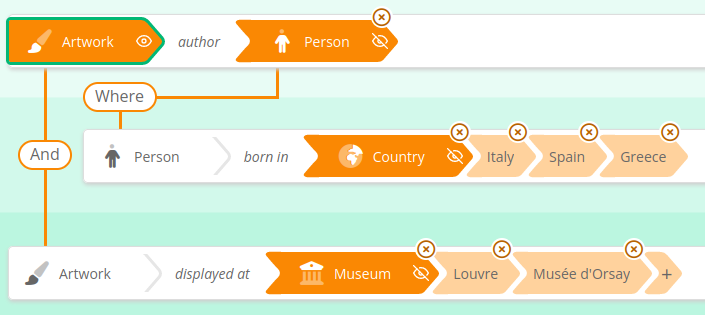
Values selection
Sparnatural offers currently 6 ways of selecting a value for a criteria : autocomplete field, dropdown list, simple string value, date range (year or date precision), date range with a search in a period name (e.g. "bronze age"), or no selection at all.
Autocomplete field
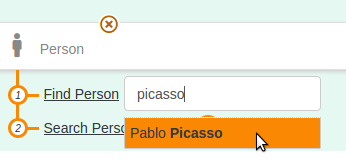
Dropdown list
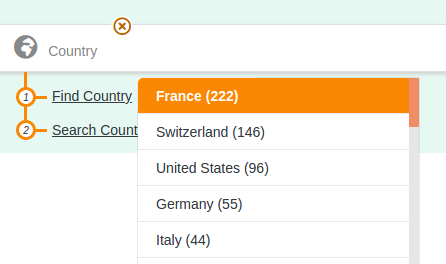
String value (text search)
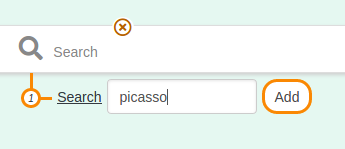
Date range (year or date precision)
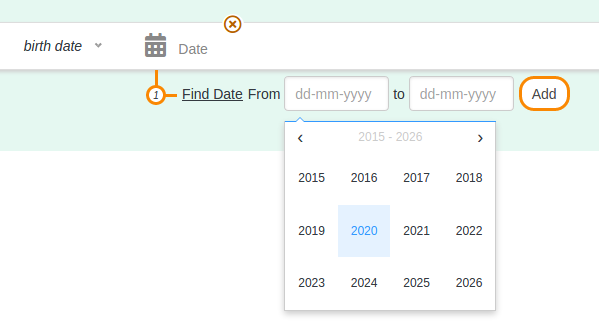
Date range with search in period name (chronocultural periods)
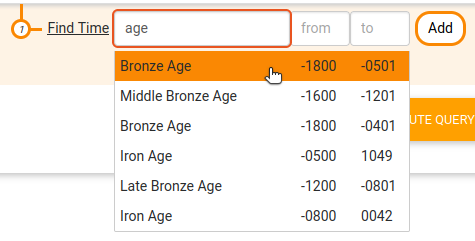
(this requires data from Perio.do, a gazeeter of periods for linking and visualizing data)
Boolean selection
No value selection
This is useful when a type a of entity is used only to navigate the graph, but without the ability to select an instance of these entities.
Multilingual
Sparnatural is multilingual and supports displaying labels of classes and properties in multiple languages.
Support for OPTIONAL and FILTER NOT EXISTS
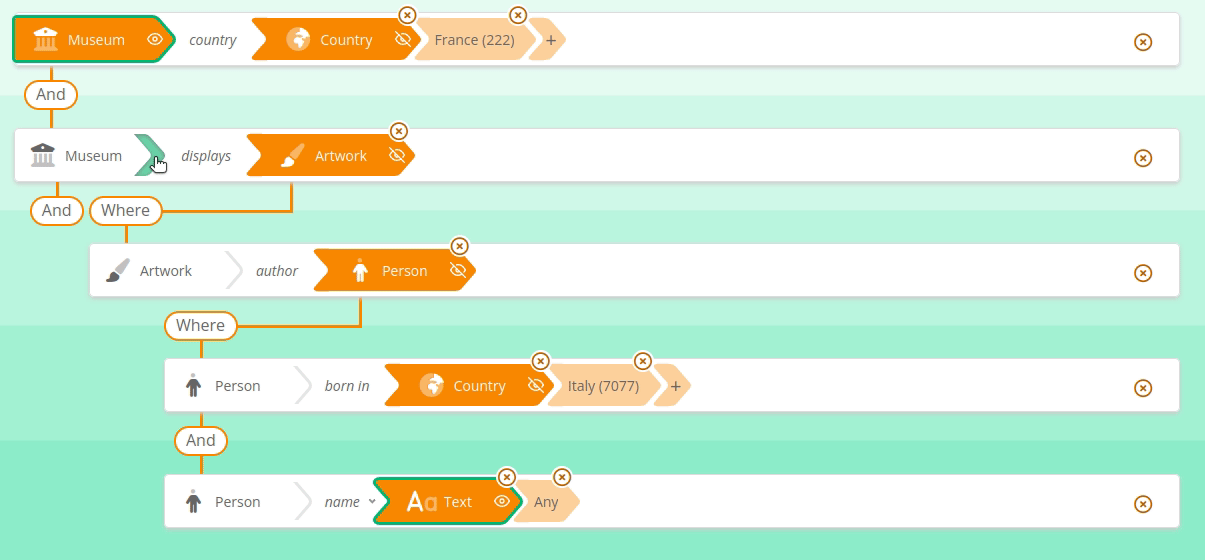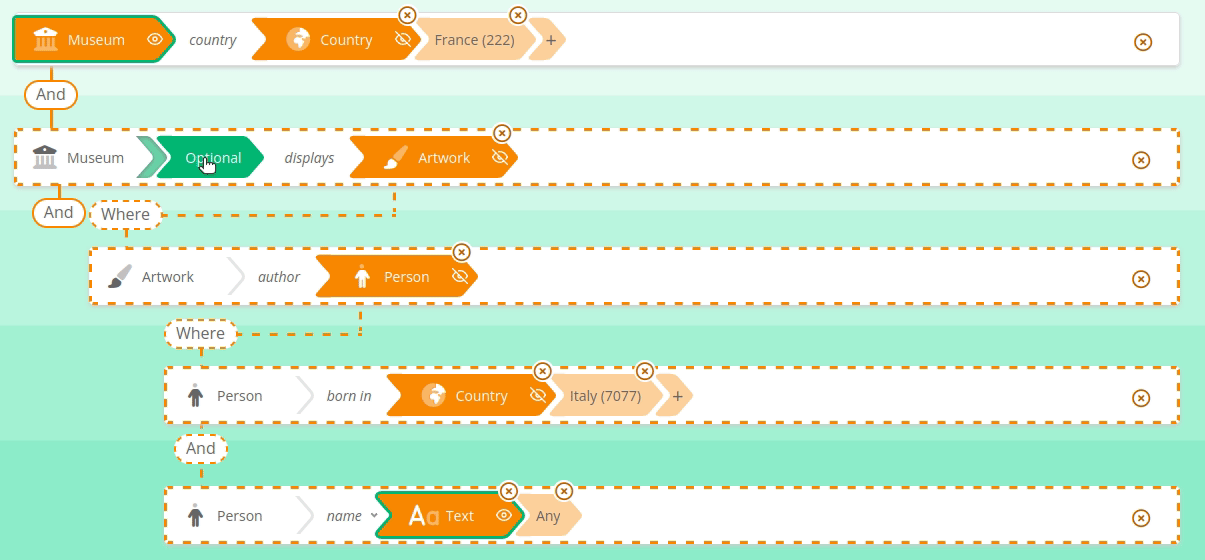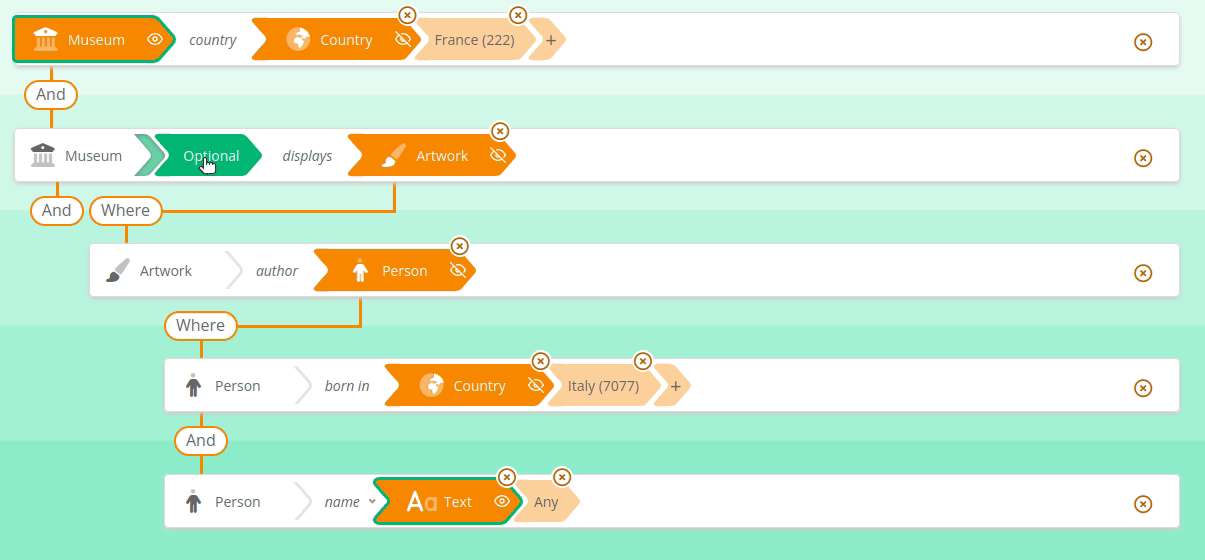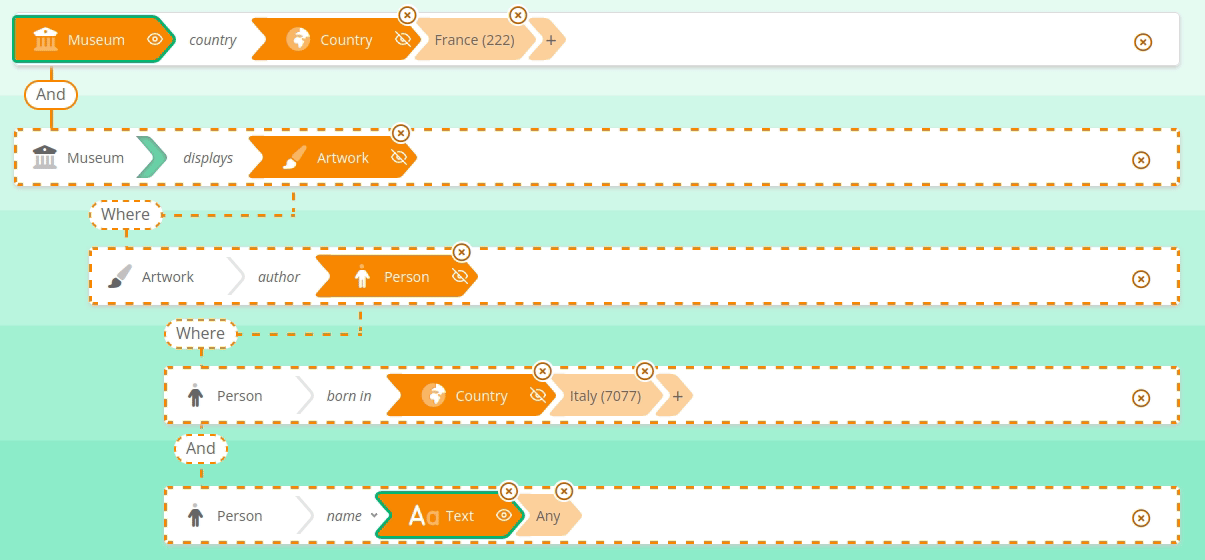
Sparnatural supports the OPTIONAL and FILTER NOT EXISTS {} keywords applied to a whole "branch" of the query.
See here how to search for French Museums and the name of Italian painters they display, if any :
Limitations
No UNION or BIND, etc.
Sparnatural does not support the creation of UNION, SERVICE, BIND, etc...
SPARQL endpoint needs to be CORS-enabled
To send SPARQL queries to a service that is not hosted on the same domain name as the web page in which Sparnatural is included, the SPARQL endpoint needs to allow Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS). But we have SPARQL proxies for those who are not, don't worry ;-)
Integration
Specification of classes and properties
The component is configurable using a an OWL configuration file editable in Protégé.. Look at the specification files of the demos to get an idea.
Alternatively one can also use a JSON(-LD) ontology file. A JSON(-LD) configuration file contains :
Class definition
{
"@id" : "http://dbpedia.org/ontology/Museum",
"@type" : "Class",
"label": [
{"@value" : "Museum", "@language" : "en"},
{"@value" : "Musée","@language" : "fr"}
],
"faIcon": "fas fa-university"
},
Property definitions with domains and ranges
{
"@id" : "http://dbpedia.org/ontology/museum",
"@type" : "ObjectProperty",
"subPropertyOf" : "sparnatural:AutocompleteProperty",
"label": [
{"@value" : "displayed at","@language" : "en"},
{"@value" : "exposée à","@language" : "fr"}
],
"domain": "http://dbpedia.org/ontology/Artwork",
"range": "http://dbpedia.org/ontology/Museum",
"datasource" : "datasources:search_rdfslabel_bifcontains"
},
Using font-awesome icons
It is possible to directly use font-awesome icons in place of icons embedded in your application :
"faIcon": "fas fa-user",
How to integrate Sparnatural in a webpage
Look at this page in the wiki documentation.
Map the query structure to a different graph structure
Map classes or properties in the config to a corresponding SPARQL property path or a corresponding class URI, using the sparqlString JSON key, e.g. :
{
"@id" : "http://labs.sparna.fr/sparnatural-demo-dbpedia/onto#bornIn",
"@type" : "ObjectProperty",
...
"sparqlString": "<http://dbpedia.org/ontology/birthPlace>/<http://dbpedia.org/ontology/country>",
},
Then call expandSparql on the sparnatural instance by passing the original SPARQL query, to replace all mentions of original classes and properties URI with the corresponding SPARQL string :
queryString = sparnatural.expandSparql(queryString);
Previous
Open Legal Lab 2022
Next project

